WFP Full Form: The World Food Programme (WFP) is the food-assistance branch of the United Nations, the world’s largest humanitarian organization, the largest one focused on hunger and food security, and the biggest provider of school meals. It is the largest humanitarian organisation in the world and the largest provider of school meals. WFP was founded in 1961 and is headquartered in Rome, with offices in 80 countries. As of 2021, it assisted over 128 million people in over 120 countries and territories.
WFP is a well-known humanitarian organisation that works to combat hunger worldwide by providing emergency food assistance and working with communities to improve nutrition. Throughout this article, we provide detailed information about WFP, like the History of WFP, objectives, structure, members & much more.
| Page Index 1 WFP Overview 2 What is WFP? 3 Objectives 4 WFP Work 5 Where WFP Work 6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
WFP Overview
This section briefly summarises WFP (World Food Programme). Let’s have a look.
| WFP | World Food Programme |
| Headquarters | Rome, Italy |
| Formation | 19 December 1961 |
| Secretary-General | Rome, Italy |
| Type | An intergovernmental organization, Regulatory body, Advisory board |
| Website | https://www.wfp.org/ |
| Member | 36 Member States |
What is WFP?
The World Food Programme is the world’s largest humanitarian organization, saving lives in emergencies and using food assistance to build a pathway to peace, stability and prosperity for people recovering from conflict, disasters and the impact of climate change.
Funding
- WFP operations are funded by voluntary donations, principally from governments around the globe and also from corporations and private donors.
- In 2019, funding was a record US $8 U.S.llion, of which the most critical donors were the u.s. ($3.4 billion) and Germany ($886.6 million). Contributions were insufficient to hide identified needs of food-insecure populations, with a funding gap of US$4.1 billion.
History
- WFP was established in 1961 after the 1960 Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Conference, director of the US FooU.S.for Peace Programmes when George McGovern proposed establishing a multilateral food aid programme.
- WFP launched its first programmes in 1963 by the FAO and, therefore, the UN GenU.N.al Assembly on a three-year experimental basis, supporting the Nubian population at Wadi Halfa in Sudan. In 1965, the programme was extended to an unbroken basis.
Mission of WFP
The World Food Programme (WFP) is dedicated to eradicating global hunger and malnutrition by providing food assistance to those in need and supporting sustainable development initiatives to tackle the underlying causes of food insecurity. Through immediate aid during crises, rebuilding efforts post-disaster, promoting sustainable agriculture, advocating for supportive policies, and assisting refugees and displaced persons, WFP aims to ensure everyone has access to the nourishment required for a healthy and productive life.
Read also:
Objectives
- The World Food Programme (WFP) is the leading humanitarian organization protecting lives and changing lives, delivering food assistance in emergencies and working with communities to achieve higher nutrition and build resilience.
- As the international community has committed to ending hunger and achieving food safety and enhanced nutrition by 2030, one in nine people worldwide still doesn’t have enough to eat.
- Food and food-related assistance lie at the guts of the trouble to interrupt the cycle of poverty and hunger.
WFP Work
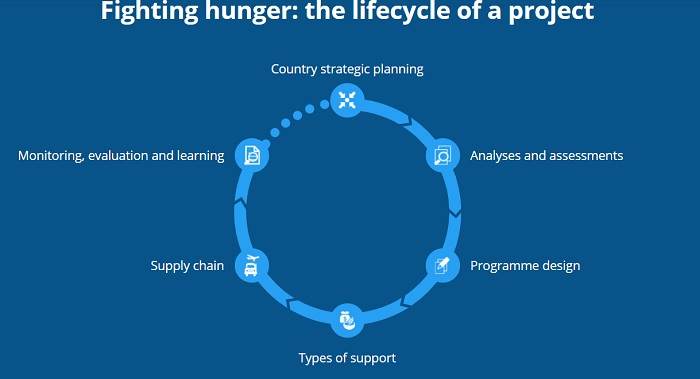
Our support to over 80 countries spans a broad range of activities to save and change lives, with the last word goal of a world with zero hunger. Within this, we concentrate on supporting governments and populations in mitigating the impact of threats, including conflict, climate shocks and other disasters, and developing sustainable livelihoods that may build self-reliance and resilience. Planning and style are essential elements of every project, as is thorough monitoring and evaluation in ensuring we meet the requirements of the people we serve and in learning where we will further strengthen our impact.
Where WFP Work
| Countries | Countries |
| Afghanistan | Kyrgyzstan |
| Algeria | Lao People’s Democratic Republic |
| Angola | Lebanon |
| Armenia | Lesotho |
| Bangladesh | Liberia |
| Benin | Libya |
| Bhutan | Madagascar |
| Bolivia (Plurinational State) | Malawi |
| Burkina Faso | Mali |
| Burundi | Mauritania |
| Cambodia | Mozambique |
| Cameroon | Myanmar |
| The central African Republic | Namibia |
| Chad | Nepal |
| China | Nicaragua |
| Colombia | Niger |
| Congo | Nigeria |
| Cuba | Pakistan |
| Côte d’Ivoire | Palestine |
| Democratic People’s Republic of Korea | Peru |
| The Democratic Republic of the Congo | Philippines |
| Djibouti | Rwanda |
| Dominican Republic | Sao Tome and Principe |
| Ecuador | Senegal |
| Egypt | Sierra Leone |
| El Salvador | Somalia |
| Eswatini | South Sudan |
| Ethiopia | Sri Lanka |
| The Gambia | Sudan |
| Ghana | Syrian Arab Republic |
| Guatemala | Tajikistan |
| Guinea | Tanzania |
| Guinea-Bissau | The Caribbean |
| Haiti | The Pacific |
| Honduras | Timor-Leste |
| India | Togo |
| Indonesia | Tunisia |
| Iran (the Islamic Republic of) | Turkey |
| Iraq | Uganda |
| Jordan | Yemen |
| Kenya | Zambia |
| Zimbabwe |
Read also:
The challenge faced by WFP
WFP has many problems to solve on its way to its goal of helping people around the world get food. Getting enough money from gifts that people give freely is always hard, especially since the need is growing. Working in areas with a lot of violence and insecurity makes it very hard to get help to people who need it. Droughts and natural disasters caused by climate change also make food shortages and insecurity worse. Also, bad infrastructure and logistical problems make it harder to get help to places that are hard to reach. Instability in politics and society makes it harder for the WFP to do its job and help people where they need it the most.
Conclusion
Internationally, the World Food Program (WFP) is leading the fight against hunger and poor diet. WFP is still committed to its goal to provide important food aid and promote sustainable development, even though it faces many problems, such as a lack of funds and difficulty navigating dangerous areas. With determination and new ideas, the World Food Program (WFP) keeps making big steps toward its final goal of ending hunger around the world, which has a good effect on many lives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What is WFP?
A. The World Food Programme (WFP) is the leading humanitarian organization saving lives and changing lives, delivering food assistance in emergencies and working with communities to improve nutrition and build resilience.
Q. How many countries are in WFP?
A. The United Nations World Food Programme (WFP) is the world’s largest humanitarian agency fighting hunger worldwide. On average, WFP aims to reach more than 90 million people with food assistance in more than 70 countries.
Q. Is the WFP an NGO?
A. The WFP is funded by voluntary donations, mainly from governments and companies and private donors. It is one of three U.N. fU.N.aid organizations based in Rome. Its sister bodies are the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD).
Q. Who funds the WFP?
A. Governments are the principal funding source for WFP; the organization receives no dues or portions of the UN assU.N.sed contributions. On average, over 60 governments underwrite humanitarian and development projects, and all government support is voluntary.

