Many people have questions about NGOs, the NGO Full Form, the different types of NGOs, how they work, the top NGOs in India, and other topics. Do you want detailed information about them and want to learn more about NGOs? This article will undoubtedly help you. So, to begin, an NGO is an organisation that is formed independently of the government and stands for Non-Governmental Organization. It is a non-profit, volunteer organisation formed to improve the social structure, children, the poor, the environment, and so on. Its work to improve socioeconomic conditions and empower people.
Table of Contents
What is an NGO?
NGOs full form Non-Governmental Organizations and are independent organisations that are not affiliated with the government, though they may collaborate with government agencies. They are typically philanthropic organisations that work to improve social or human welfare. NGOs are frequently formed to fill a void left by governments that cannot or will not act.
For example, an NGO may provide relief following a natural disaster, provide the best education to rural areas, some shelter to stay and their health or assist in the delivery of medical supplies to a war-torn country. Non-Government organizations may also fight for environmental protection or human rights. There are literally thousands of non-governmental organisations (NGOs) working on a wide range of issues around the world.
NGOs Legal Acts
In India, NGOs can be registered under three main legal acts:
1. Societies Registration Act, 1860
(For registering a Society)
2. Indian Trusts Act, 1882
(For registering a Trust)
3. Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013
(For registering a Section 8 Company — non-profit company)
Other related statutes (optional but common):
- Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA), 2010 – for receiving foreign funding
- Income Tax Act, 1961 (12A, 80G) – for tax exemptions
Also Read: How to register an NGO under NITI Aayog I Step by step Guide
History of NGO
The origins of international non-governmental organizations (NGOs) may be traced back to the late 18th century, when an estimated 1,083 NGOs were in existence by 1914. They were very important in efforts like ending slavery and giving women the right to vote. The World Disarmament Conference in 1932–1934 was its peak. The term became more well-known after the United Nationswas created in 1945.
Also Read: WHO Mental Health Action Plan to 2030
Article 71 of the UN’s charter gives advisory standing to groups that are not part of a government. In 1950, the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) of the United Nations added to this list by saying that international NGOs are groups that were not created by international laws. As Agenda 21 shows, NGOs became more well-known in the fight for sustainable development.
The reworking of welfare states in Western countries has sped up the growth of NGOs. This growth accelerated around the world after communist systems fell apart, which is in line with the Washington Consensus. Globalization in the 20th century made NGOs even more important by giving them a way to fight back against corporate projects with social, developmental, and long-term goals. Events like the World Social Forum and the Earth Summit in 1992 made it clear how important it is for foreign NGOs to work together to solve environmental problems and promote long-term growth. Nowadays, a big part of NGOs’ activity and effect is their ability to network with groups in other countries.
What are the types of NGOs?
There are many questions in our mind, such as how many types of NGOs and their orientation and level of operation can be classified. So we are providing complete knowledge about many types of NGOs; let’s look.
NGOs are classified by their orientation, which means the type of activities an NGO undertakes, such as activities involving consumer protection, human rights, health, environmentalism, or development and level of operation, which means the scale at which an organization works: regional, local, national, or international.
Also Read: Accelerating Gender Equality (SDG 5) in India by 2025
Other acronyms commonly used to describe non-governmental organisations are:
| BINGO (Business-friendly international NGO) | CSO (Civil society organization) |
| ENGO (Environmental NGO) | DONGO (Donor-organized NGO) |
| GONGO (Government-organized non-governmental organization) | GSO (Grassroots Support Organization) |
| INGO (International NGO) | MANGO (Market advocacy NGO) |
| NGDO (Non-governmental development organization) | NNGO (Northern (UK) NGO) |
| PANGO (Party NGO — addressing political matters) | PVDO (Private voluntary development organization) |
| Quango (Quasi-autonomous NGO) | SBO (Social benefit organization) |
| SCO (Social change organization) | SNGO (Southern (UK) NGO) |
| TANGO (Technical assistance NGO) | TNGO (Transnational NGO) |
| YOUNGO (Youth NGOs – advocating for youth rights) | – |
Orientation of NGOs
| Orientation | Description |
|---|---|
| Charities | They involve NGOs directed at meeting the requirements of disadvantaged people and groups. |
| Service | It involves NGOs that give healthcare (including family planning) and education. |
| Participation | It includes self-help projects involving local tools, land, money, materials, or labour. |
| Empowerment | It aims to help poor people know the political, social, and economic factors influencing their lives and raise awareness of their power to control them. |
Objectives of NGOs
Non-governmental organisations (NGOs) can be a powerful force for positive change in the world. They work to improve people’s lives in their communities and around the world. The following are the objectives of NGOs:
- To fight for human rights
- To offer humanitarian assistance
- To promote long-term development
- To support indigenous peoples’ cultures – To protect the environment
Also Read: Role of Indian NGOs in UN SDGs
Level of Operation – NGOs
| Level of Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Community-based organizations (CBOs) | A popular initiative can increase the awareness of the urban poor, helping them get their right to services and giving such services. |
| City-wide organizations | It includes commerce and industry chambers, business coalitions, ethnic or educational groups, and community organizations. |
| State NGOs | It includes state-level organizations, associations, and groups, and national and international NGOs guide some state NGOs. |
| National NGOs | It is an NGO that survives in only one country; they are rare. These include national organizations such as YMCAs and YWCAs, professional associations, and similar groups. |
| International NGOs (INGOs) | It ranges from secular agencies, such as to save the children, to religious groups. They may fund local NGOs, institutions and projects and implement projects. |
Advantages of an NGO
We are sharing the following advantages of commencing an NGO in India:
- Improve Literacy level
- Improve standards of living
- Innovative approaches
- Better communication
- It enhances the ability of rural women and teenagers to lead.
- It encourages youngsters and rural women to be more creative.
- It promotes unemployed young people and rural women to start businesses.
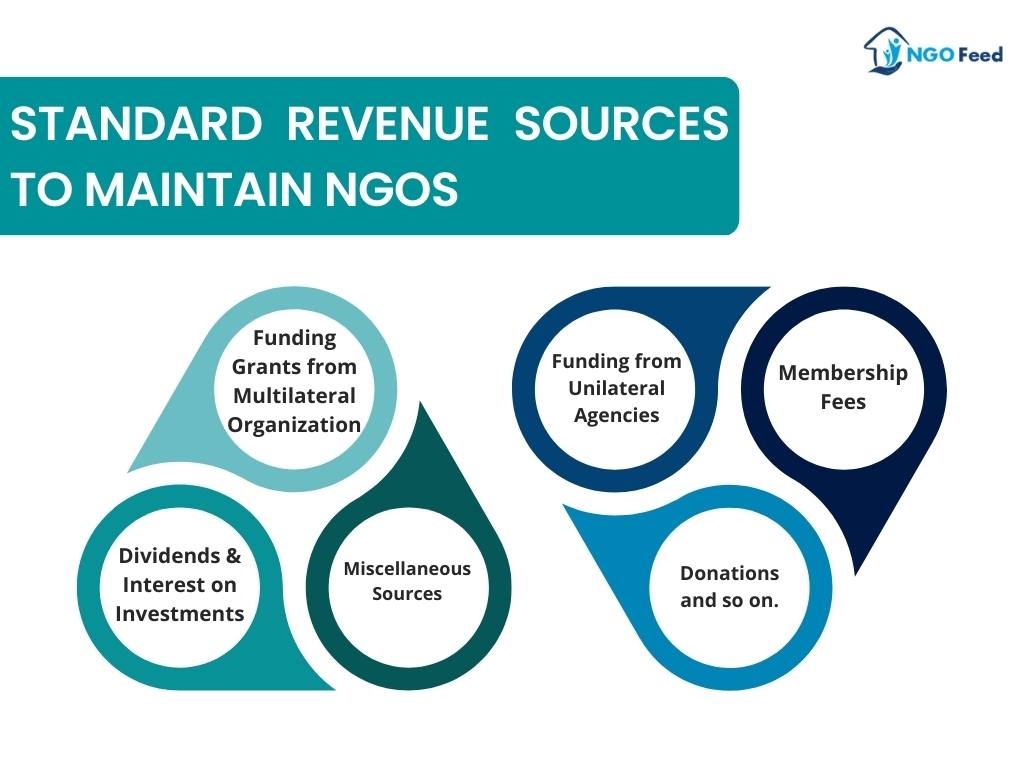
Standard Revenue Sources to Maintain NGOs
They can accept donations from private individuals, for-profit corporations, charitable foundations, and governments of all levels, including local, state, federal, and international. They can also charge membership dues and sell goods and services because they are nonprofit organisations. In this section, you can get information about the Standard Revenue Sources to Maintain NGOs. Let’s have a look.
Also Read: The Role of UNFPA in India
Conclusion
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are the most powerful force behind solving issues internationally among communities. Having a history dating back to the late 18th century, NGOs have gone through the process of evolution and are now regarded as key forces for change. They are now campaigning for human rights, providing humanitarian aid to those in need, and preserving the future of global development.
The NGO’s different persuasions and levels of operations let them satisfy numerous needs, from local projects to humanitarian undertakings of international dimensions. They have the potential to increase literacy levels, enhance the quality of life, and promote the development of skills such as creativity and self-actualization. It makes money from fundraising, membership dues, and trading goods and services. Attired in multiple colors and always optimistic, NGOs act as agents of positive transformation, continuing to overcome challenges and making a sustainable impact in communities globally.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. What is the Full Form of an NGO?
A. NGO stands for Non-Governmental Organization.
Q. What is NGO work?
A. NGOs take up and execute projects to promote the welfare of the community they work with, and they work to address various concerns and issues prevailing within society.
Q. What is the advantage of an NGO?
A. The advantages of NGOs are:
> Improve Literacy level
> Improve standards of life
> Innovative approaches
> Better communication
Q. What are the types of NGOs?
The types of NGO are:
Local NGOs
National NGOs
International NGOs
Charitable NGOs
Service NGOs
Development NGOs
Advocacy NGOs
Participatory NGOs
Emergency/Humanitarian NGOs
Operational NGOs
Hybrid NGOs
Human rights NGOs
Environmental NGOs
Health NGOs
Educational NGOs
Women’s rights NGOs
Rural development NGOs
Child welfare NGOs
Refugee NGOs
Peacebuilding NGOs
Digital rights NGOs
Cultural NGOs
Donor-funded NGOs
Membership-based NGOs
Self-funded NGOs
Corporate-sponsored NGOs
Government-organized NGOs (GONGOs)
Faith-based NGOs
Secular NGOs
Professional NGOs
Community-based organizations (CBOs)
Quasi-autonomous NGOs (QUANGOs)
Business-influenced NGOs (BINGOs)
Mutual-interest NGOs (MINGOs)
Donor-influenced NGOs (DINGOs)










Halp my trust
NGO work is very impactful to human lives. This is commendable.
Thanks for your valuable message.