UNEP Full Form: The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) coordinates environmental issues within the United Nations system. Maurice Strong, its first director, founded UNEP and later the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm in June 1972. Its mandate is to give leadership, deliver science and develop solutions to various issues, including climate change, the control of marine and terrestrial ecosystems, and green economic development.
UNEP Headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya, UN Environment Programmer is led by a Senior Management Team chaired by our Executive Director. The organization also develops international environmental agreements, publishes and promotes ecological science and helps national governments achieve ecological targets. We work in our divisions, regional, liaison and out-posted offices, plus a growing network of collaborating centers of excellence.
Table of Contents
UNEP Overview
Here in this section, we provide a short overview of UNEP (United Nations Environment Programmer). Let’s have a look:
History Of UNEP
In the 1970s, the need for environmental governance at a global level was not wholly accepted, especially by developing nations. Any argued that environmental concerns were not a priority for countries in poverty. Canadian diplomat Maurice Strong’s leadership convinced multiple developing nations’ governments that they needed to prioritize this issue.
Structure of UNEP
Below have mentioned, UNEP’s structure includes eight divisions:
- Science Division: It aims to provide scientifically reliable environmental assessments and information for sustainable development. It reports on the state of the global environment, evaluates policies, and provides an early warning of emerging environmental threats. It is in charge of monitoring and registering the background regarding the 2030 Agenda and Sustainable Development Goals.
- Policy and Programme Division: It makes the policy and programme of the UNEP. This division ensures other divisions are organized.
- Ecosystems Division: It helps countries conserve, restore and manage their ecosystems. It addresses the environmental causes and consequences of disasters and conflicts. It allows governments to reduce pollution from land-based activities, increase resilience to climate change, and think about the environment in their development planning.
- Economy Category: It tries to get large businesses more environmentally informed. It has three main categories: Chemicals and Health, Energy and Climate, and Resources and Markets.
- Governance Affairs Office reserves member states and other relevant groups to use UNEP’s work. The office works with UNEP’s governing body, the United Nations Environment Assembly, a subsidiary organ, the Committee of Permanent Representatives, and manages its meetings. It helps strengthen the Assembly’s visibility, authority and impact as an authoritative voice on the environment.
- Law Division: It supports to development of environmental law. The law department aims to improve cooperation between lawmakers around the world who are making ecological laws. Works with countries to combat environmental crime and meet international environmental commitments.
- Communication Division: develops and disseminates UNEP’s messages. It delivers them to authority to individuals through digital and traditional media channels.
- Corporate Services Division: It handles UNEP’s corporate interests, such as management and exposure to financial risk.
Read also:
Objectives of UNEP
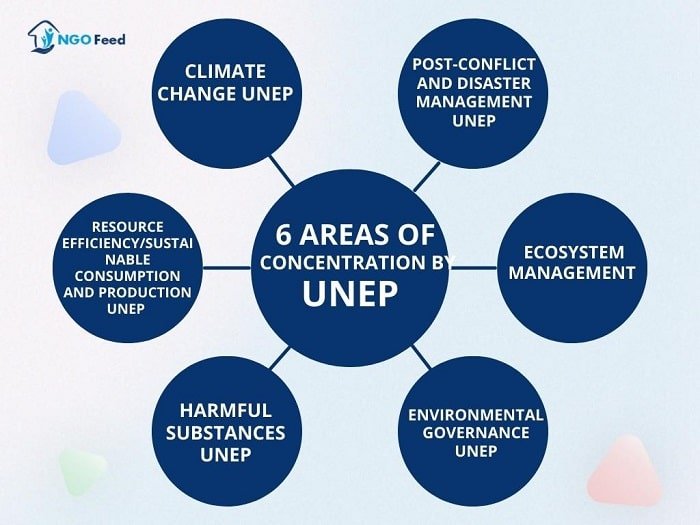
- Climate change
- Ecosystem management
- Disasters and conflicts
- Environmental governance
- Resource efficiency
- Chemicals and waste
- Environment under review
UNEP: 6 Areas of Concentration
As part of its transition to results-based management, UNEP reorganised its work plan into 6 major areas. Scientific data, the UNEP mission, and priorities emanating from global and regional forums influenced the selection of six areas of specialisation.
Funding of UNEP
- UNEP relies on voluntary contributions for 95% of its funding.
- The Environment Fund is UNEP’s primary source of flexible funds.
- Earmarked funds enable UNEP to expand programs in more countries and with more partners.
- Main providers of earmarked funds include the Global Environment Facility, Green Climate Fund, and European Commission.
- UNEP works in partnerships with governments, the private sector, civil society, and other UN entities globally.
- It brings together partners to address common environmental challenges, such as through the UN Environment Assembly.
UNEP and India
- India has had a good relationship with UNEP ever since it began.
- Indian UNEP has been there since 2016, and the Ministry for Environment, Forests, and Climate Change is in charge of coordinating their work.
- India and UNEP have worked together on many projects, mostly in the environmental field.
- UNEP has praised India’s work, such as the International Solar Alliance, and named Prime Minister Narendra Modi a Champion of the Earth.
- The High Commissioner of India for Kenya speaks for Kenya at UNEP.
- India gives the UNEP about $100,000 every year.
- In 2019, India became a part of the Climate and Clean Air Coalition. UNEP is in charge of running the coalition.
- India has gotten help from UNEP to develop renewable energy, make industry cleaner, protect biodiversity, slow down climate change, and teach people about the environment.
Conclusion
Since its start, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has been a strong voice for global environmental problems. It works hard to educate, empower, and motivate countries to improve their quality of life while protecting the planet for future generations. With its strong framework, clear strategic goals, and focused areas of focus, UNEP continues to lead the way in solving the world’s most important environmental problems. UNEP stays at the top of global environmental governance and action by working with companies, governments, civil society groups, and other UN organisations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the full form of UNEP?
The full form of the UNEP United Nations Environment Programme.
Where is the headquarters of UNEP located?
Nairobi, Kenya.
How many countries are in UNEP?
193 UN Member States.
Is UNEP an organization?
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) was established in 1972 to guide and coordinate environmental activities within the United Nations (UN) system.
Who is the head of UNDP?
Achim Steiner
Read also:










Good to read about the good work you are doing, I am very much interested in knowing more about your activities in West Africa and also to be part of your workforce in the region, thanks for this platform.
Thanks for your valuable comment
We are going to organise a Yagna in India for Environment Protection and conservation.
Great
I am a retired engineer from Govt of India. I want to contribute in programmes of UNEP but do not know the the mythology.
I need help in this regard.
You can contact the UNEP on their official website.