“The proliferation of NGOs can be seen as a symptom of deeper processes of globalization, such as the retreat of the state from the social provision and the growth of a global civil society.”
– Saskia Sassen, scholar and author
In an era of democratic essence, where we have put forward the idea of equality and liberty as key ideas, global civil society has emerged on the same plane. It is debatable whether it is a symbol of solidarity or a failure of the nation-state.
So, let’s start the discussion on ‘Global Civil Society’.
Global civil society refers to a network of individuals and organizations that operate across borders to address social and environmental issues. This network includes NGOs, activist groups, social movements, and other civil society organizations.
History of Global Civil Society
The concept of global civil society emerged in the late 20th century as a result of the increasing globalization and the growth of civil society organizations. Here is a brief history of the development of global civil society:
- The 1960s and 1970s: The civil rights movement, women’s rights movement, and other social movements of the 1960s and 1970s contributed to the growth of civil society organizations. These organizations focused on promoting social justice, human rights, and democratic values.
- The 1980s and 1990s: The fall of the Soviet Union and the emergence of new democracies in Eastern Europe and Latin America led to a proliferation of civil society organizations. At the same time, advances in communication technology, such as the internet and social media, made it easier for civil society organizations to connect and collaborate across borders.
- The 2000s and beyond: The 21st century has seen a rapid expansion of global civil society, with organizations working on issues such as climate change, poverty, and human rights abuses. The United Nations and other international organizations have recognized the important role of civil society in addressing these issues, and have sought to engage civil society organizations in their work.
Today, global civil society includes a wide range of organizations, from large international NGOs to small grassroots groups. These organizations work on a variety of issues, from promoting democracy and human rights to addressing global health crises and environmental challenges. While the concept of global civil society is still evolving, it is clear that civil society organizations have a critical role to play in shaping the future of our global community.
Is Global Civil Society a threat to the nation-state?
Global civil society can play an important role in promoting social justice and democratic values, but it can also pose a threat to the state in several ways:
- Weakening of state sovereignty: The growth of global civil society can challenge the traditional notion of state sovereignty, as civil society actors increasingly operate beyond the control of individual states. This can lead to tension between the state and civil society, particularly in authoritarian regimes where the state seeks to maintain tight control over all aspects of society.
- The undermining of state legitimacy: Global civil society can also undermine the legitimacy of the state by exposing corruption, human rights abuses, and other forms of misconduct. By holding the state accountable, civil society can create pressure for reform and change.
- Disrupting state policies: Civil society can also disrupt state policies and initiatives, particularly when these policies are seen as unjust or oppressive. Civil society actors may engage in protests, civil disobedience, and other forms of activism to challenge state policies and demand change.
- Fragmentation of society: The growth of civil society can also lead to the fragmentation of society, as different groups pursue their own agendas and interests. This can create tension and conflict within society, as different groups compete for resources and influence.
- While global civil society can pose a threat to the state, it can also play a positive role in promoting democracy, social justice, and human rights. By providing a platform for marginalized communities to voice their concerns, civil society can help to create more inclusive and participatory societies. However, it is important for civil society actors to work in a constructive and collaborative manner, and to respect the rule of law and democratic principles.
Formation of Global Civil Society
The formation of global civil society is a complex process, involving a range of actors, networks, and institutions. Here are some key factors that have contributed to the formation of global civil society:
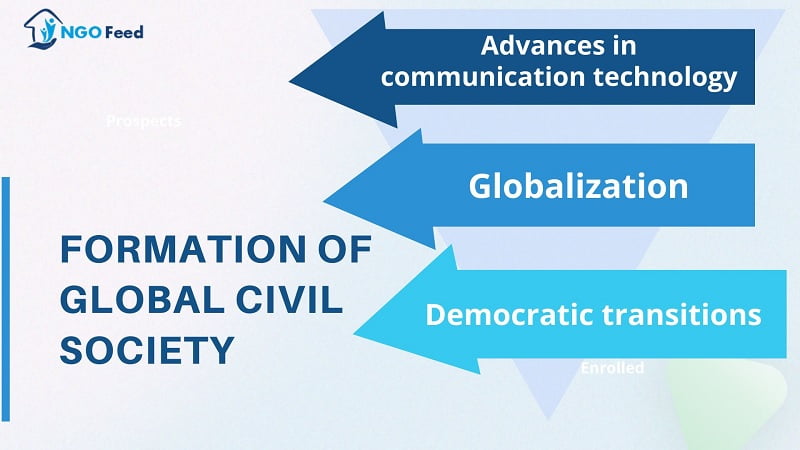
- Advances in communication technology: Advances in communication technology, such as the internet and social media, have made it easier for civil society organizations to connect and collaborate across borders. These technologies have enabled the rapid dissemination of information and ideas, and have helped to foster a sense of global community among civil society actors.
- Globalization: The process of globalization has led to increased interdependence between countries and regions, creating a need for transnational cooperation and collaboration. This has led to the emergence of global civil society organizations, which work to address global issues such as climate change, human rights, and poverty.
- Democratic transitions: The transition to democracy in many countries has created new opportunities for civil society organizations to operate freely and engage in political processes. This has led to the growth of civil society organizations and has contributed to the formation of global civil society.
Benefits of Global Civil Society
The benefits of global civil society are many. Here are some key benefits:
- Promoting democratic values: Global civil society organizations play a critical role in promoting democratic values such as freedom of expression, transparency, and accountability. By holding governments and other powerful actors accountable, civil society organizations can help to promote more democratic and inclusive societies.
- Advancing social justice: Civil society organizations can also work to advance social justice, by advocating for the rights of marginalized groups and promoting a more equitable distribution of resources.
- Addressing global issues: Global civil society organizations can work together to address global issues such as climate change, poverty, and human rights abuses. By collaborating across borders and sharing knowledge and resources, civil society organizations can make a significant impact on these issues.
- Providing a voice for marginalized groups: Global civil society organizations can provide a platform for marginalized groups to voice their concerns and advocate for their rights. By giving voice to those who are often excluded from traditional political processes, civil society can help to create more inclusive and participatory societies.
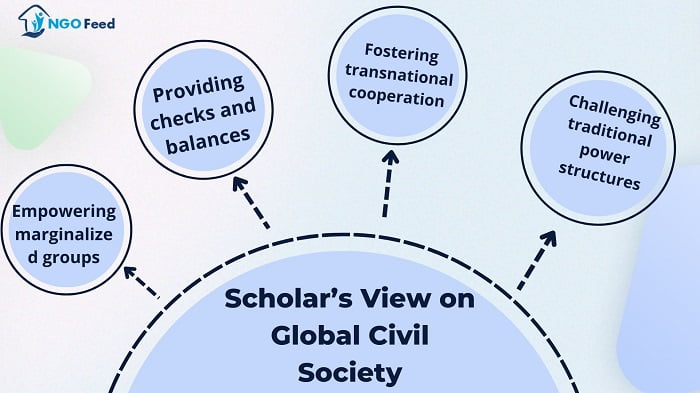
Scholar’s View on Global Civil Society
Scholars have varied views on global civil society, but many see it as a critical force in promoting democracy, social justice, and sustainable development. Here are some key perspectives:
- Empowering marginalized groups: Many scholars see global civil society as a way to empower marginalized groups that have been excluded from traditional political processes. By providing a platform for these groups to voice their concerns and advocate for their rights, civil society can help to create a more inclusive and participatory democracy.
- Providing checks and balances: Global civil society can also provide a check on the power of governments and corporations, holding them accountable for their actions and advocating for more transparent and accountable decision-making processes.
- Fostering transnational cooperation: Civil society organizations can facilitate transnational cooperation and collaboration, bringing together individuals and organizations from different countries and regions to work together on common goals.
- Challenging traditional power structures: Some scholars see global civil society as a way to challenge traditional power structures and promote alternative forms of governance that prioritize the needs and rights of marginalized groups.
Conclusion
However, some scholars also caution that global civil society can be co-opted by powerful actors, or can become fragmented and ineffective. It is important for civil society actors to work in a coordinated and strategic manner, and to engage in dialogue with other stakeholders, including governments and corporations. Additionally, civil society must be vigilant in upholding democratic principles and human rights and avoiding the pitfalls of exclusion and fragmentation.

