The IFAD Full form is an International fund for agricultural development and it is an international financial institution and a specialised agency of the United Nations that works to address poverty and hunger in rural areas of developing countries. It is the only multilateral development organization that focuses on rural economies, food security and climate change.
Headquartered in Rome, Italy, IFAD is involved in over 200 projects across nearly 100 countries. It funds and sponsors initiatives that improve land and water management, develop rural infrastructure, train and educate farmers in more efficient technologies, build up resilience against climate change, enhance market accessibility, and more.
Table of Contents
History
One of the primary outcomes of the 1974 World Food Conference was the establishment of IFAD as an international finance agency by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 32/107 (30 December 1977). It is a part of the UN Development Group and has its headquarters in Rome, Italy. Gilbert F. Houngbo, a Togolian, serves as the president of the IFAD. He was chosen for a second, four-year term in 2021 after being selected in 2017.
IFAD Overview
| IFAD Full Form | International fund for agricultural development |
| Headquarters | Rome, Italy |
| Formation | 15 December 1977 |
| Managing Director | Gilbert Houngbo |
| Method | Social science research |
| Website | www.ifad.org |
IFAD Opportunities
Agriculture has a track record of reducing poverty. Compared to growth in other sectors, GDP growth from agriculture is more successful at reducing poverty. Growth in agriculture in sub-Saharan Africa eliminates poverty up to 11 times more quickly than growth in other industries.
IFAD-funded programmes have demonstrated that rural people may escape poverty provided they have access to money, markets, technology, and knowledge.
But our effort has benefits beyond simply boosting rural residents’ economic development. Additionally, it encourages inclusivity and gender equality increases the capability of neighbourhood associations and communities, and increases climate change resistance.
Our work is essential to achieving the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development by supporting initiatives that revitalise rural regions and fighting for the needs of underprivileged rural residents.
Read also:
Challenges
The most pressing problems facing humanity cannot be put off due to the expanding world population, which will reach 9 billion by 2050, the widening wealth and poverty divide, and the intensifying struggle for limited resources.
In the most remote areas of developing countries and in unstable conditions, where few development organisations venture, IFAD works where poverty and hunger are at their worst.
We have established a partnership-focused, cost-efficient strategy that produces outcomes. Our development strategy, which links farmers and underprivileged rural people to markets and services so they can increase their productivity and income, is centred on small-scale agriculture.
IFAD (India)
Since 1979, IFAD has had a presence in India. In India, the organisation works to improve poor people’s access to technological advancements in agriculture, financial services, natural resources, and value chains.
| Particular | Description |
|---|---|
| Work | It also works to share knowledge and lessons learned about nutrition security & poverty alleviation. |
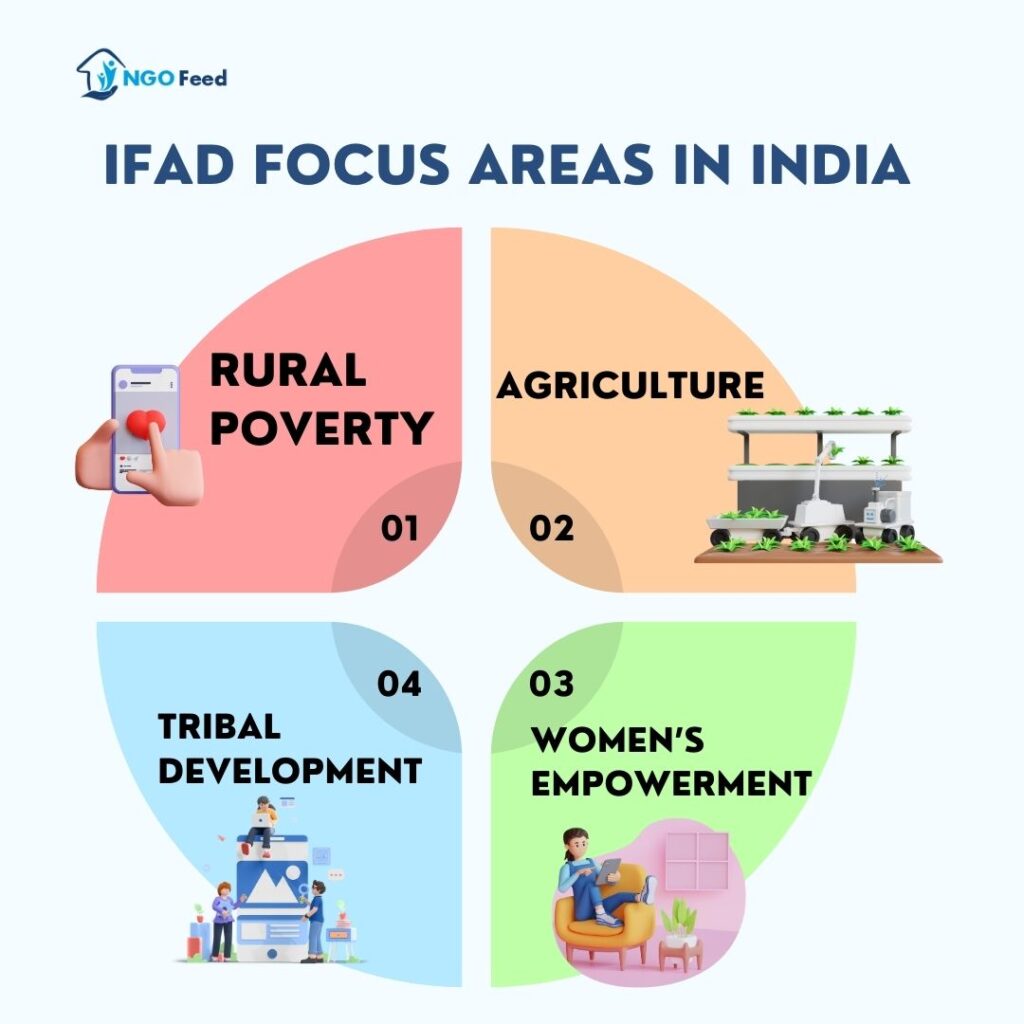
| Main Focus | In India, the emphasis is on tribal communities, smallholder farmers, women, scheduled castes, etc. |
| Located | IFAD is located in New Delhi. |
| Nodal Agency | The Department of Economic Affairs, Finance Ministry, GOI is the IFAD’s nodal agency in India. |
IFAD Focus Areas in India
Read also:
Initiatives and facilities of IFAD
As the world focuses on the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, IFAD is supporting several innovative programmes and platforms aimed at achieving a world free of hunger and poverty. In the below table, you can get information about the IFAD initiatives and facilities.
| Adaptation for Smallholder Agriculture Programme (ASAP) | Indigenous Peoples Assistance Facility (IPAF) |
| Agri-Business Capital (ABC) Fund | The Financing Facility for Remittances (FFR) |
| China-IFAD South-South and Triangular Cooperation Facility | Diaspora Investment in Sustainable Rural Youth Entrepreneurship in Mali |
| IFAD Crisis Response Initiative | Global gender transformative approaches initiative for women’s land rights |
| IFAD’s Rural Poor Stimulus Facility | Gender Transformative Mechanism in the Context of Climate Adaptation |
| Pacific Islands Rural and Agriculture Stimulus Facility | Joint Programme on Accelerating Progress towards the Economic Empowerment of Rural Women – JP RWEE |
| The Climate and Commodity Hedging to Enable Transformation (CACHET) | International Aid Transparency Initiative |
| A platform for Agricultural Risk Management (PARM) | National Designated Authorities partnership platform |
| Insurance for Rural Resilience and Economic Development (INSURED) | Rural Resilience Programme |
| International Land Coalition (ILC) | The Smallholder and Agri-SME Finance and Investment Network |
| Facility for Refugees, Migrants, Forced Displacement and Rural Stability (FARMS) | Private Sector Financing Programme |
Conclusion
An important organization in the fight against poverty and hunger in emerging countries’ rural areas is IFAD, which stands for the International Fund for Agricultural Development. It has been around since 1977 and main goal is to give rural areas more power by funding and starting projects that improve infrastructure, agriculture, and the ability to handle climate change. IFAD’s work in almost 100 countries has shown that putting money into agriculture can help people get out of poverty and make their lives better. Even though there are problems like more people and fewer resources, IFAD is still dedicated to its goal of establishing long-lasting rural economies and completing the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the IFAD Full Form?
The IFAD Full Form is an International fund for agricultural development.
When is IFAD established?
The IFAD is established on 15 December 1977.
What does IFAD do?
It works to address poverty and hunger in rural areas of developing countries.
How many countries are in IFAD?
IFAD has 177 Member States from all regions of the world, including developing, middle, and high-income countries committed to ending rural poverty.
What is the headquarter of IFAD?
IFAD headquarters is located in Rome, Italy.









