ECB Full Form: European Central Bank, It is one of the most powerful financial institutions in the world, and it is playing an important role in the economic stability and policy-making within the Eurozone. It is the central bank for the euro and is responsible for controlling monetary policy among the 19 member countries of the Eurozone. In this article, You will explore ECB Full Form: History, Work, Achievement etc.
The ECB is assigned to take care of price stability within the Eurozone to keep inflation low, stable, and predictable. Its headquarters is in Frankfurt, Germany, and works under a framework that prioritizes transparency, independence, and accountability.
Table of Contents
History of the European Central Bank
The ECB was founded on June 1, 1998, in preparation for the launch of the euro on January 1, 1999. Its establishment was a turning point in the development of European integration with the goal of setting up monetary policy among participating EU member states. The ECB succeeded the European Monetary Institute (EMI), which pawed the way of the groundwork for the introduction of the euro and the foundation of the ECB.
ECB Organizations
In the history of European integration, the establishment of the ECB marked a crucial turning point. It originated from the Maastricht Treaty, which established the framework for the establishment of the euro and the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU). The ECB doesn’t need any support from national governments and other EU organizations, which is necessary to maintain its credibility and effectiveness in implementing monetary policy.
Three primary bodies work for the ECB decision-making structure:
- The Governing Council: This is the main decision-making body of the ECB. It consists of the six members of the Executive Board and the governors of the national central banks of the Eurozone countries. The Governing Council conducts meetings two times in a month to discuss and make decisions on monetary policy.
- The Executive Board: The President, the Vice-President, and four more members is the part of the Executive Board, which is in charge of running the ECB on a daily basis. Their appointments are for eight-year terms that are not renewable.
- The General Council: the governors of every national central bank in the European Union, as well as the president and vice president of the European Central Bank, are members of the General Council, but with a more restricted function and limited role. It assists in the evolution of the euro and executes monetary policies across EU members outside the eurozone.
ECB functions and responsibilities
ECB’s functions and responsibilities as a Central Bank for Eurozone countries are below.
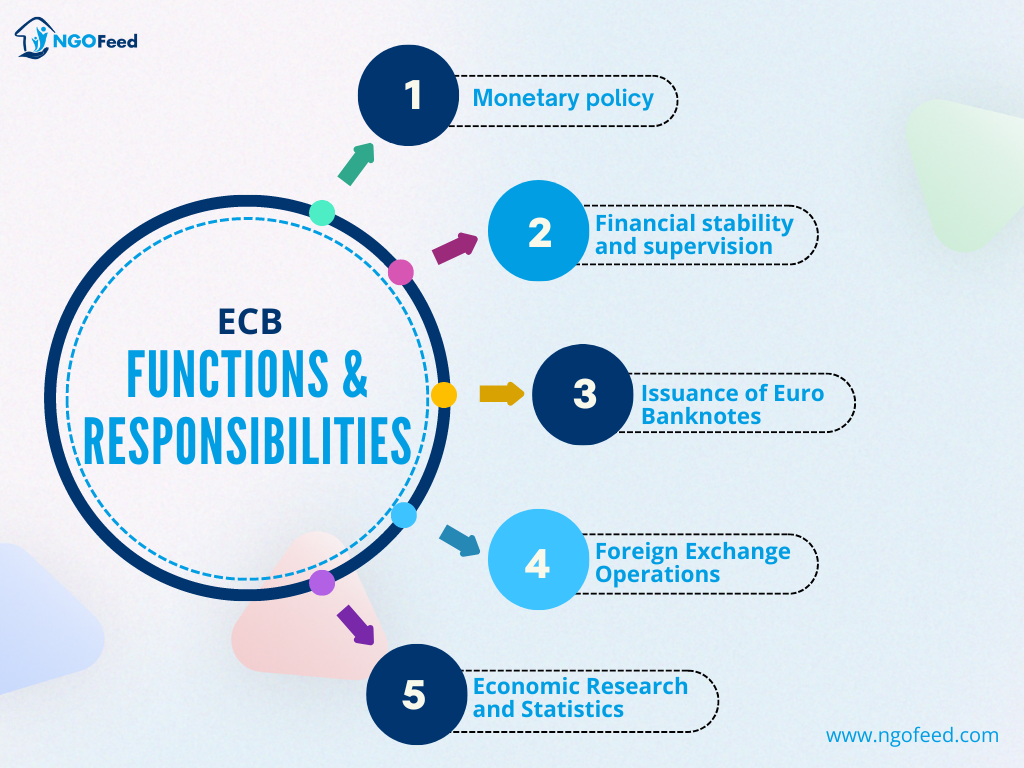
1. Monetary policy
The creation and execution of monetary policy for the Eurozone is the main duty of the ECB. By keeping inflation rates below but near 2% over the medium term, it aims to keep price stability. The European Central Bank (ECB) uses a variety of monetary policy measures to do this, such as conducting open market operations, establishing key interest rates, and supplying liquidity to the banking system.
2. Financial stability and supervision
In order to keep the financial system stable, the ECB is playing a crucial role. With the creation of the Single Supervisory Mechanism (SSM) in 2014, the ECB was given direct control over major banks operating in the Eurozone. This supervisory function makes sure banks follow good procedures, efficiently manage risks, and withstand shocks to the economy.
3. Issuance of Euro Banknotes
Euro banknotes are issued by the European Central Bank (ECB) in cooperation with national central banks. To deter counterfeiting, it guarantees a steady supply of banknotes and monitors their quality and security features.
4. Foreign Exchange Operations
To preserve exchange rate stability, the ECB oversees the Eurozone’s foreign currency reserves and carries out foreign exchange operations. To solve global economic issues, it also works with other central banks and international organizations.
5. Economic Research and Statistics
To help inform its policy decisions, the ECB carries out a thorough investigation and analysis of the economy. In addition, it gathers and distributes statistical information about the economy of the Eurozone, which is helpful to the public, scholars, and policymakers.
European Central Bank achievements
Since its founding, the European Central Bank (ECB) has achieved several noteworthy achievements, such as:
| Introduction of Euro | The ECB managed the smooth transition from separate national currencies to the euro, which is currently the second most traded currency in the world. |
| Crisis Management | During the European sovereign debt crisis, financial markets were stabilized by implementing policies like the Securities Markets Programme (SMP) and Outright Monetary Transactions (OMT) into place. |
| Quantitative Easing | Starting the Asset Purchase Programme (APP) to encourage lending and provide liquidity to boost the Eurozone economy. |
| Banking Supervision | In 2014, the ECB established the Single Supervisory Mechanism (SSM) to enhance the stability and safety of the European financial sector through strict scrutiny and financial stability. |
| Digital Euro Initiative | The ECB is exploring issuing a digital euro to supplement cash, aiming to provide a reliable and efficient digital currency for daily transactions in response to the digitized economy. |
Facts and Figures
| Established | June 1, 1998 |
| Headquarters | Frankfurt, Germany |
| Current President | Christine Lagarde (since November 2019) |
| Number of Member Countries | 19 Eurozone countries |
| Governing Council Members | 25 (19 national central bank governors and 6 Executive Board members) |
| Official Currency | Euro (€) |
| Total Assets | Approximately €4.7 trillion |
European Central Bank Awards
| Central Banking Awards | It recognizes its excellence in various areas, including central banking, economic policy, and innovation. |
| The ECB has been commended for its transparency and communication efforts. | he ECB has been commended for its transparency and communication efforts. |
| Financial Times and The Banker Awards | The ECB has been featured in the Financial Times and The Banker awards for its innovative approaches to monetary policy and crisis management. |
Conclusion
The growth and stability of the Eurozone economy are strongly dependent on the European Central Bank. The European Central Bank (ECB) has played a key role in maintaining price stability, monitoring banks, and handling financial crises since its founding in 1998. Its broad scope and autonomous standing allow it to contribute to the general economic health of the Eurozone and successfully negotiate challenging economic environments. The European Central Bank is steadfast in its commitment to keeping price stability and promoting sustainable economic growth, even as it continues to adjust to new challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the European Central Bank (ECB)
(ECB) European Central Bank is the main bank for the euro and controls monetary policy within the Eurozone, which comprises of 19 of the 27 member states of the European Union that have embraced the euro as their single currency.
When was the ECB established?
The ECB was founded on June 1, 1998, and it started operating completely on January 1, 1999, which was also the day the euro was introduced
What are the responsibilities of the ECB?
Maintaining price stability within the Eurozone, managing foreign exchange operations, making sure payment systems run smoothly, and supervising and policing financial institutions are among the core duties of the European Central Bank (ECB).
How does the ECB maintain price stability?
The ECB wants to keep inflation low but near 2%. To achieve this goal, it applies multiple kinds of monetary policy tools, including interest rate setting and money supply management.
How does the ECB impact the global economy?
monetary policy decisions of ECB have an impact on currency rates, economic growth, and international financial markets. Economists, politicians, and investors all over the world are closely observing its behaviour.
Read also :

