UNCDF Full Form: The United Nations Capital Development Fund was created to fund public and private finance for the poor in 46 least-developed countries (LDCs). UNCDF provides a “last mile” finance model that unlocks public and private resources, especially at the household level, to reduce poverty and support local economic development with its capital mandate and tools. It is the last stage where resources available for the product are scarce, market failures are most evident, and those who benefit from national development are excluded. Today UNCDF is functioning in additional than 46 member countries. It works with public and private finance for the poor in the world.
| Index 1 UNCDF Overview 2 History 3 Main Function of UNCDF 4 What makes UNCDF different? 5 The Least Developed Countries by UNCDF 6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
UNCDF Overview
This section briefly overviews the United Nations Capital Development Fund (UNCDF). Let’s have a look.
| UNCDF | United Nations Capital Development Fund |
| Headquarters | New York, USA |
| Formation | 1966 |
| Executive Secretary | Preeti Sinha |
| Website | www.uncdf.org |
| Works | 46 least developed countries |
History
Created by the General Assembly in 1966 to promote economic development, UNCDF was officially established as “an autonomous organisation within the United Nations” with the aim of “assisting developing countries in the development of their economies”, which complements existing sources of capital support using grants and loans”.
In 1973, the Governing Council focused UNCDF’s activities toward “first and least developed countries” and began focusing on the world’s least developed countries in 1974.
Read also:
Main Function of UNCDF
UNCDF’s financing models work through three channels
- Inclusive digital economies: This connects individuals, families and small businesses to a financial ecosystem that catalyses participation in the local economy and provides the tools to break out of poverty and manage an economic life;
- Local development finance: This enables localities through financial decentralisation, innovative municipal finance and structured project finance to drive local economic expansion and sustainable development
- Investment finance: This provides catalytic financial structuring, de-risking and capital deployment for SDG impact and domestic resource mobilisation.
What makes UNCDF different?
UNCDF is a small but focused organisation with a primary job to do. With a unique capital mandate in the United Nations Development System, the UNCDF helps keep finance flowing to the least developed and excluded people, places and small enterprises. UNCDF shows every day how small amounts of official development assistance can help LDCs leverage public and private resources for maximum impact in the last mile.
UNCDF is innovative – It can help introduce new and innovative technologies, financing tools and partnerships to tackle inequality and exclusion in LDCs;
UNCDF is catalytic – In the rapidly changing development finance landscape, UNCDF can support LDCs to use Official Development Assistance (ODA) to take advantage of other sources of finance. UNCDF’s innovative finance model and public-private partnerships can also help in risk-free markets to encourage investment and promote sustainable development;
UNCDF promotes inclusion – UNCDF helps LDCs build more inclusive and resilient communities and economies by assisting them in targeting areas and sectors that other development finance institutions have not yet focused on. It is crucial to meet the challenges of the 2030 Agenda to leave no one behind.
The Least Developed Countries by UNCDF
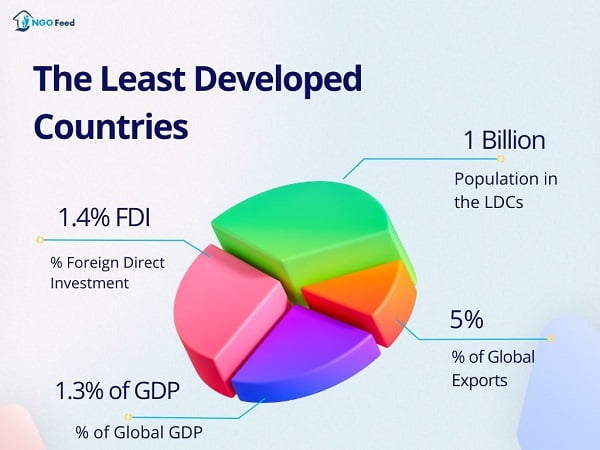
UNCDF and India
- UNCDF collaborates with the Odisha government to promote financial empowerment and gender equality among women in the state.
- A memorandum between the Odisha government’s Department of Mission Shakti and UNCDF is signed to advance initiatives such as Mission Shakti Living Lab, aimed at enhancing women’s financial well-being.
- UNCDF, in partnership with NITI Aayog, Atal Innovation Mission, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and the Rabo Foundation, launches a South-South innovation platform in India.
- The platform facilitates the exchange of insights, investments, and innovation, with the rollout of the first AgriTech Challenge cohort as part of an Agri-tech programme.
UNCDF Funding
- UNCDF is autonomously funded and affiliated with UNDP.
- Its funding is separate, and sourced from member states, foundations, and the private sector.
- Contributions support initiatives for sustainable development and poverty reduction.
- Funds enable projects in financial inclusion and local development.
- Flexible funding model ensures responsiveness to emerging needs.
Conclusion
For least developed countries (LDCs), the United Nations Capital Development Fund (UNCDF) is an essential instrument for boosting economic growth and reducing poverty. With its unique focus on offering “last mile” financing, UNCDF gives people and communities the tools they need to take part in local economies, which promotes growth and stability for everyone. The UNCDF makes the most of its resources to have the biggest effect possible and to solve the problems of sustainable development. It does this through creative financing models and smart relationships. Its work shows how focused investments can bring about good changes and move the global development plan forward.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Full form of UNCDF?
UN Capital Development Fund (UNCDF).
How many countries are in the UN Capital Development Fund?
There are 46 least-developed countries.
Who is the head of the UNCDF?
Preeti Sinha is the Executive Secretary of the UN Capital Development Fund.
Read also:

