OECD Full Form: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. OECD could be a forum of states describing themselves as committed to democracy and free enterprise, providing a platform to check policy experiences, identify good practices and coordinate domestic, seek answers to common problems, and international policies of its members.
Today, OECD member countries account for three-fifths of global GDP, three-quarters of global trade, more than 90% of global official development assistance, half of global energy consumption, and 18% of the global population. Throughout this article, you will get complete information about the OECD full form, such as how they work, its objectives, history, members etc.
OECD Overview
The OECD is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 38 member countries
| OECD | Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) |
| Headquarters | Paris, France |
| Formation | 16 April 1948 |
| Secretary-General | Mathias Cormann |
| Type | Intergovernmental organisation |
| Website | https://www.oecd.org/ |
| Member | 36 Member |
What is OECD?
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is a global organisation that works to improve policies for better lives. They draw on 60 years of experience and insights to better prepare the planet of tomorrow. They aim to shape policies that foster prosperity, equality, opportunity, and well-being.
- OECD provides a stage for its member countries to match policy experiences, identify and share best practices, seek answers to common problems and coordinate domestic and international policies of its member nations.
- The OECD member states collectively included 62.2% of worldwide nominal GDP (US$49.6 trillion) and 42.8% of global GDP (Int$54.2 trillion) at buying power parity in 2017.
- OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries.
History
- The Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC) was formed in 1948 to administer American and Canadian aid within the framework of the European Recovery Program for reconstructing Europe after war II.
- In the 1950s, the OEEC provided the framework for negotiations to determine conditions for putting in place a European trade Area to bring the European Economic Community of the six and the other OEEC members together on a multilateral basis. In 1958, a European atomic energy Agency was founded under the OEEC.
- OEEC was renamed the OECD in 1961 when the USA and Canada joined to reflect a broader membership.
OECD Objectives
The objectives of the OECD involve fostering economic development and cooperation and fighting poverty by promoting financial stability.
- It also assures that the environmental impact of growth and social development is often considered.
- Over the years, OECD has built the standards of living in multiple countries and added to the expansion of world trade.
Organisational Structure of OECD

Read also:
OECD Functions and Responsibilities
The OECD plays a critical role in promoting global economic stability. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) publishes and updates a model tax convention as a template for allocating taxation rights between countries.
- The OECD publishes economic reports, statistical databases, analyses, and forecasts on global economic growth.
- The group investigates the impact of social issues on economic growth and makes recommendations to promote global economic growth. These recommendations also consider the environmental concerns associated with economic development.
- The organisation works to eradicate bribery and other forms of financial crime worldwide.
- The OECD also keeps a “blacklist” of countries that it considers to be uncooperative tax havens.
- It also took efforts in the G-20 countries to eliminate tax evasion by profitable corporations. It also encourages the G-20 to promote tax reforms.
Principles of OECD
- Openness, transparency, and inclusiveness.
- Engagement and participation in policymaking and service delivery.
- Creation of a data-driven culture in the public sector.
- Protecting privacy and ensuring security.
- Leadership and political commitment.
- Coherent use of digital technology across policy areas.
- Effective organization and governance frameworks for coordination.
- Strengthening international cooperation among governments.
- Development of clear business cases.
- Reinforcement of ICT project management capabilities.
- Procurement of digital technologies.
- Establishment of a legal and regulatory framework.
Member Countries
There are currently (May 2021) 38 members of the OECD.
| Country | Membership | Geographic location |
| Australia | 7 June 1971 | Oceania |
| Austria | 29 September 1961 | Europe |
| Belgium | 13 September 1961 | Europe |
| Canada | 10 April 1961 | North America |
| Chile | 7 May 2010 | South America |
| Colombia | 28 April 2020 | South America |
| Costa Rica | 25 May 2021 | North America |
| Czech Republic | 21 December 1995 | Europe |
| Denmark | 30 May 1961 | Europe |
| Estonia | 9 December 2010 | Europe |
| Finland | 28 January 1969 | Europe |
| France | 7 August 1961 | Europe |
| Germany | 27 September 1961 | Europe |
| Greece | 27 September 1961 | Europe |
| Hungary | 7 May 1996 | Europe |
| Iceland | 5 June 1961 | Europe |
| Ireland | 17 August 1961 | Europe |
| Israel | 7 September 2010 | West Asia |
| Italy | 29 March 1962 | Europe |
| Japan | 28 April 1964 | East Asia |
| South Korea | 12 December 1996 | East Asia |
| Latvia | 1 July 2016 | Europe |
| Lithuania | 5 July 2018 | Europe |
| Luxembourg | 7 December 1961 | Europe |
| Mexico | 18 May 1994 | North America |
| Netherlands | 13 November 1961 | Europe |
| New Zealand | 29 May 1973 | Oceania |
| Norway | 4 July 1961 | Europe |
| Poland | 22 November 1996 | Europe |
| Portugal | 4 August 1961 | Europe |
| Slovakia | 14 December 2000 | Europe |
| Slovenia | 21 July 2010 | Europe |
| Spain | 3 August 1961 | Europe |
| Sweden | 28 September 1961 | Europe |
| Switzerland | 28 September 1961 | Europe |
| Turkey | 2 August 1961 | West Asia/Europe |
| United Kingdom | 2 May 1961 | Europe |
| United States | 12 April 1961 | North America |
India and OECD
India has been engaged with the OECD since 1997 through a cooperation program, despite not being a formal member. However, it became the 27th member of the OECD’s Development Centre. In 2007, the OECD Council adopted a resolution to strengthen cooperation with India, alongside other key partners such as Brazil, China, Indonesia, and South Africa. As a Key Partner, India benefits from access to the OECD’s analysis, statistical databases, technical expertise, and analytical capacity, enhancing its policymaking capabilities and fostering international collaboration.
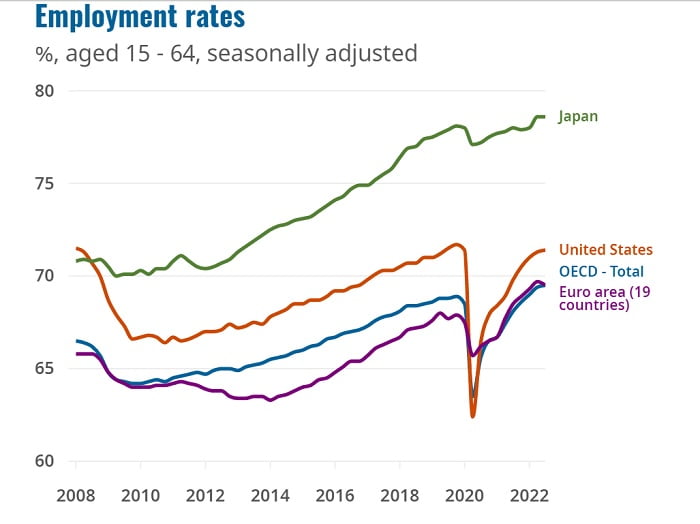
OECD Employment Rates
Read also:
OECD Funding Sources
- OECD is primarily funded by member countries.
- Contributions are based voluntarily.
- The formula considers the economic size and relative wealth of each member.
- Additional funding from contracts for specific projects or activities.
- Revenue generated from publications and other products/services.
Conclusion
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is one of the most important groups for promoting economic growth and unity between its 38 member countries. It has been around since 1961 and works to improve well-being, equality, and wealth while also tackling problems like poverty and protecting the environment. The OECD is very important to the way international economic government works because it has many important jobs, such as supporting economic stability, fighting financial crime, and making policy suggestions. The OECD is still a key player in promoting global economic growth thanks to its openness, transparency, and inclusion ideals and its work with important partners like India.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What means OECD?
A. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is an international organisation that works to build better policies for better lives.
Q. Who funds the OECD?
A. its member countries fund OECD. National contributions are based on a formula that takes into account the size of each member’s economy. Governments may also make voluntary contributions to financially support outputs in the OECD program of work.
Q. Where is the headquarter of OECD?
A. The headquarter of OECD in Paris, France
Q. How many OECD members are there?
A. There are 38 Member countries in OECD.
Is India a member of the OECD?
No, India isn’t a member of the OECD yet. This is because India is being wary about what kind of signal its membership in OECD would give to other emerging countries located in the South Asian continent. But it is a crucial partner of the OECD.



